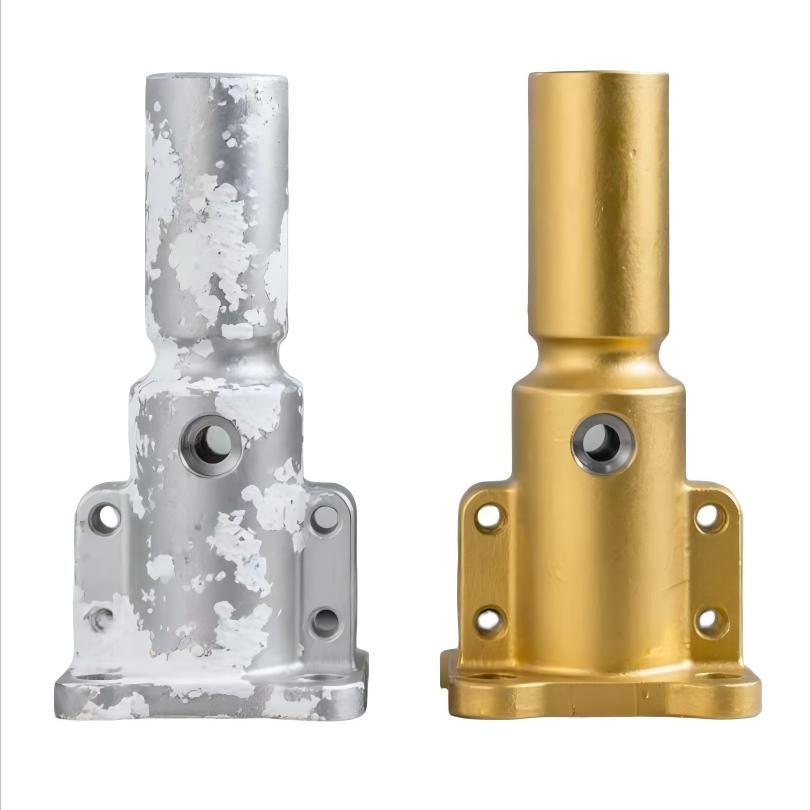
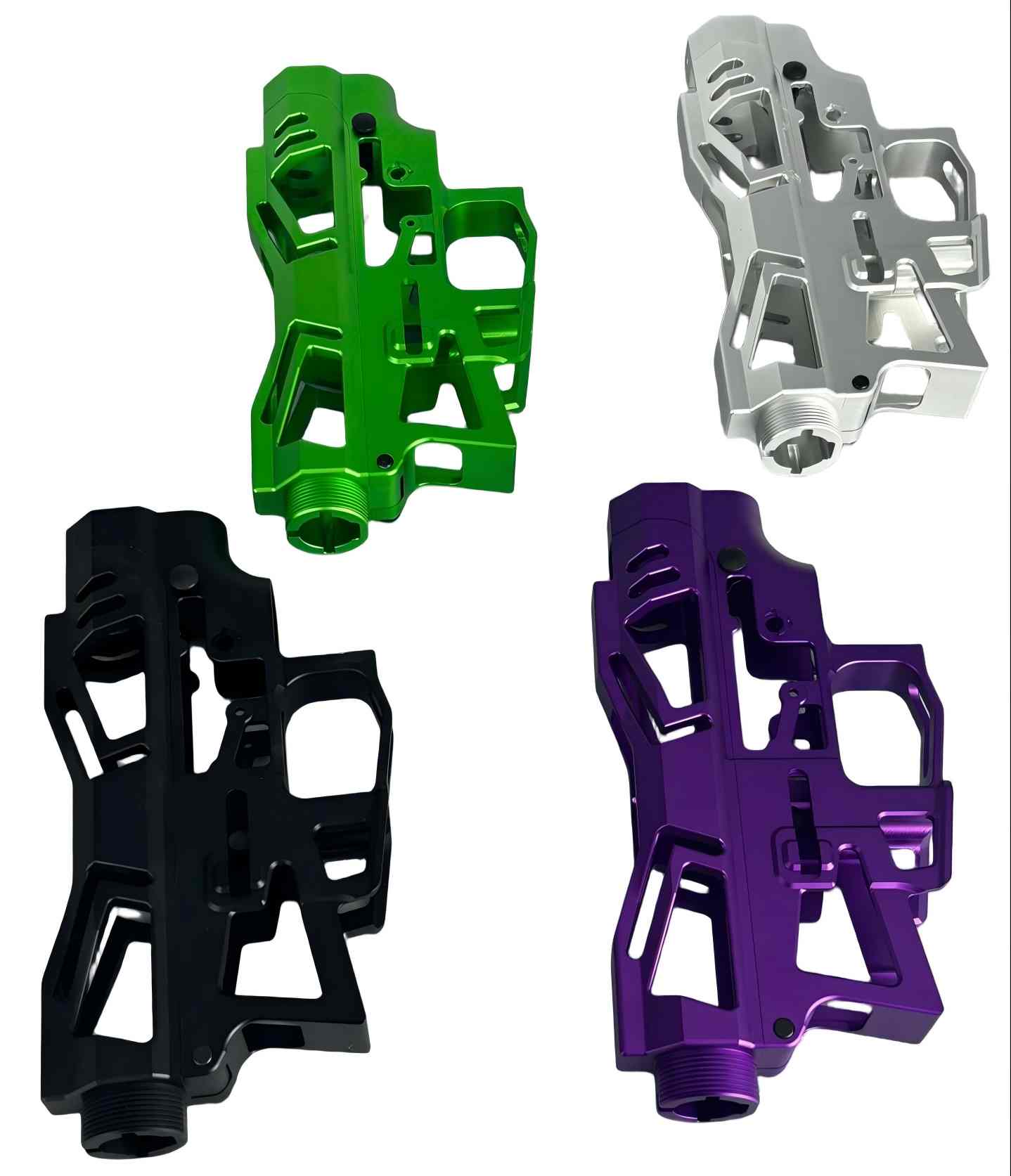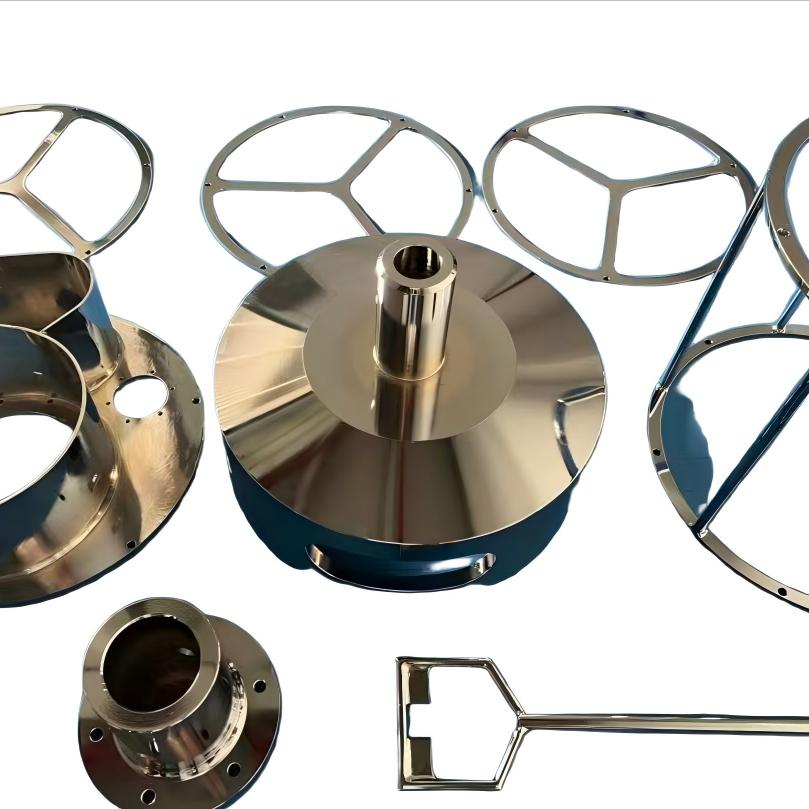

Surface Finishing
What is Surface Finishing and Why is it Critical?
Surface treatment is an industrial process used to process the surface of a part to achieve the desired properties. In simple terms, it's like applying a high-performance "coat" to a product, making it the critical step that transforms a semi-finished component into a high-quality, final product.
Its importance can be broken down into these core areas:
Extends Operational Lifespan: This is its most crucial function. The right surface finish can significantly enhance corrosion resistance (preventing rust),
wear resistance, and surface hardness.
Increase Perceived Value & Market Competitiveness: Surface finishing can impart a specific luster, color, and texture to a product, making it appear
more professional and visually appealing.
Meet Professional & Stringent Requirements: The finishing techniques can add entirely new capabilities to a product, such as electrical conductivity,
insulation,self-lubrication, or resistance to chemical corrosion.
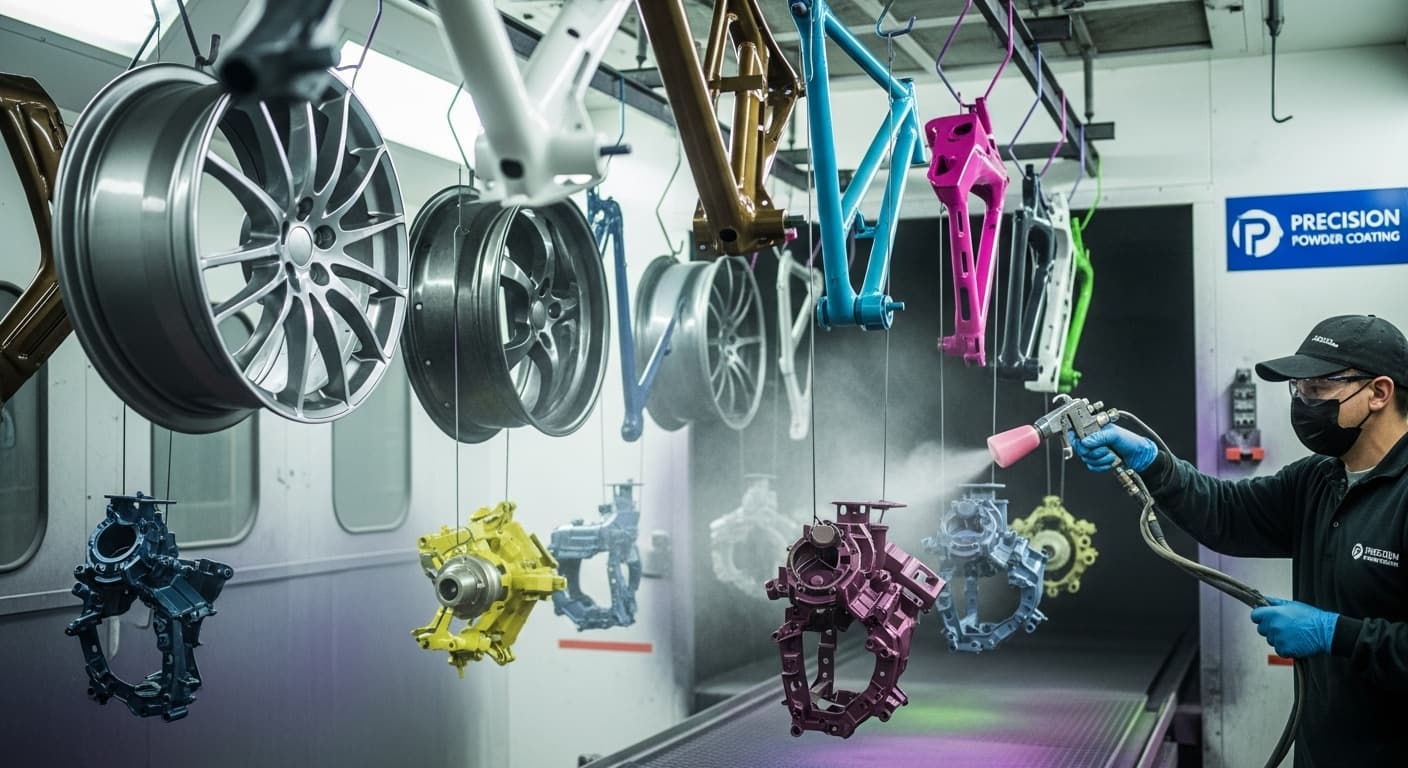

Our Comprehensive Metal Finishing Services
Surface finishing is performed to improve the surface properties of a part, including its appearance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and electrical conductivity. Below are some common surface finishing methods:
1. Anodizing
Description: Electrochemically grows a hard, protective oxide layer on aluminum to significantly improve wear resistance, corrosion resistance,
and enable dyeing.
Functions:
Improves corrosion resistance
Increases surface hardness and wear resistance
Change the appearance color, such as black, red, blue, etc.
Increases insulation
Applications: Aerospace, electronics, automotive parts, mechanical parts, etc.
2. Sandblasting (Bead Blasting)
Description: Propels abrasive media at high velocity to clean and roughen a metal surface, creating an ideal foundation for superior coating adhesion.
Functions:
Removes surface dirt, rust, and scale
Creates a rough surface to improve the adhesion of paint or coatings
Improves appearance (matte finish)
Applications: Surface pretreatment or aesthetic treatment of various metal parts, such as chassis, housings, and mechanical parts.
3. Powder Coating
Description: Forms a durable, attractive, and eco-friendly protective layer that is tougher than conventional paint via electrostatic spray thermal curing.
Function:
Improves appearance, adds color, and decorative effects
Improves corrosion and wear resistance
Protects the surface
Applications: Cases, automotive parts, furniture, mechanical equipment, etc.
4. Electroplating
Description: Deposits a metallic film on a conductive surface using electrolysis to enhance its corrosion resistance, hardness, and conductivity.
Function:
Improve corrosion resistance
Improve surface hardness and wear resistance
Change appearance and enhance decorative effect
Improve conductivity
Common electroplating types: Zinc plating, nickel plating, chrome plating, gold plating, silver plating, etc.
Applications: Various metal parts, such as fasteners, electronic components, automotive parts, and decorative items.
5. Brushing
Description: A uniform linear texture is formed on the metal surface through mechanical wear to enhance beauty and conceal minor flaws.
Function:
High-grade metallic texture that enhances the appearance.
Hides minor scratches and fingerprints.
Applications: Electronic product housings, decorative components, kitchenware, household items, etc.
6. Polishing
Description: Reduces surface roughness using mechanical or chemical means to achieve a smooth, bright, and mirror-like decorative finish.
Function:
Improves appearance and enhances gloss.
Removes surface burrs and scratches.
Reduces friction.
Applications: Decorative parts, optical devices, medical devices, molds, etc.
7. Passivation
Description: Maximizes the inherent corrosion resistance of a metal, typically stainless steel, by forming a dense, protective oxide film on its surface.
Function:
Improve corrosion resistance
Improve surface stability
Applications: Medical, aviation, food automation, automotive, semiconductors, and machinery
8. Heat Treatment
Description: Modifies a metal's microstructure through controlled heating and cooling to optimize mechanical properties like
hardness, strength, and toughness.
Applications:
Increases hardness, strength, and wear resistance
Improves toughness
Stress relief
Applications: Various metal parts, especially those requiring high strength or wear resistance.
9. Laser Marking
Description: Uses a high-energy laser beam for non-contact, permanent engraving of high-precision text or graphics onto a product's surface.
Function:
Marking part numbers, trademarks, model numbers, and other information
Providing traceability
Decorative effects
Applications: Electronic products, medical devices, tools, nameplates, etc.
Choosing the Right Surface Treatment for Your Application
Not all surface treatments are suitable for all materials. For example, anodizing is primarily used for aluminum alloys, while passivation is typically applied to stainless steel.
The choice of a surface treatment depends on the part's application, material, design requirements, cost, and specific needs for appearance and performance.
There may be compatibility issues between different surface treatments, and the selection must be made based on the specific circumstances.
If you don't find the process you want, please contact us: [email protected]
Industries We Serve with Specialized Surface Finishes
Aerospace & Defense
Medical & Pharmaceutical
Automotive
Electronics & Semiconductor
Energy
Industrial Machinery & Equipment
Our Commitment to Quality: From Substrate to Final Finish
Our process begins with a thorough understanding and meticulous preparation of your part's substrate because we know that a perfect finish originates from a flawless foundation. Throughout the treatment, we strictly adhere to industry standards, such as ASTM, by precisely controlling and continuously monitoring chemical parameters, process times, and finish thickness. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that every product we deliver is not only impeccable in appearance but also meets or exceeds your design specifications in performance. This means your products will benefit from a longer service life, enhanced reliability, and ultimately, a stronger reputation in the marketplace.
Get a Custom Quote for Your Surface Finishing Project
Start your free project evaluation and experience:
Your dedicated service consultant - tailor-made services
Easy to understand and communicate with us in a language you understand
Excellent quality and peace of mind - Expected results, guaranteed quality
All CAD files are secure and confidential.






